Results
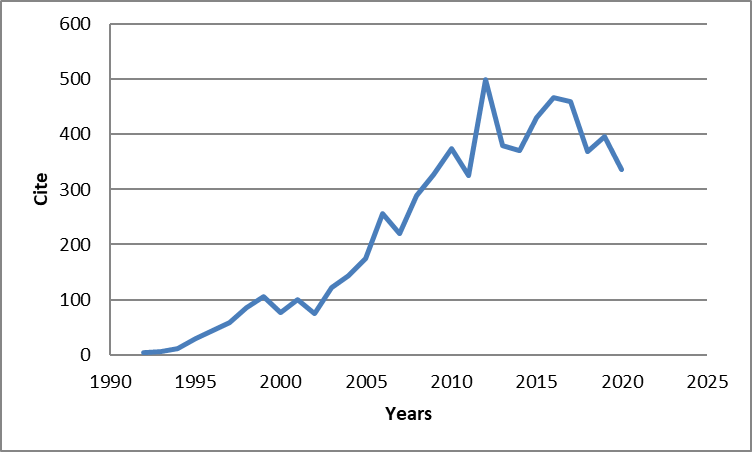
A total of 790 publications related to wrist arthroscopy were identified. The 100 highest cited papers according to number of citations can be seen in Table 1. The number of citations ranged from 35 to 180 (average, 64.74). The total number of citations was 6,474. Of the 100 articles, 37 (37%) were published between 1990 and 2000, 52 (52%) were published between 2000 and 2010, and only 11 (11%) were published between 2010 and 2020. The year with the highest total number of citations was 2012 (499) Table 2. Among the articles, 96 were written in English, and 4 were written in German.
|
Rank |
Article |
Total citations |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Triangular fibrocartilage tears |
180 |
|
2 |
Peripheral tears of the triangular fibrocartilage complex cause distal radioulnar joint instability after distal radial fractures |
140 |
|
3 |
Chronic wrist pain: spin-echo and short tau inversion recovery MR imaging and conventional and MR arthrography |
135 |
|
4 |
Magnetic resonance imaging and miniarthroscopy of metacarpophalangeal joints - Sensitive detection of morphologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis |
119 |
|
5 |
The unar fovea sign for defining ulnar wrist pain: An analysis of sensitivity and specificity |
116 |
|
6 |
Comparison of synovial tissues from the knee joints and the small joints of rheumatoid arthritis patients - Implications for pathogenesis and evaluation of treatment |
113 |
|
7 |
Scapholunate ligament reconstruction using a bone-retinaculum-bone autograft |
111 |
|
8 |
Epidemiology of musculoskeletal upper extremity ambulatory surgery in the United States |
107 |
|
9 |
Sport injuries: a review of outcomes |
106 |
|
10 |
Wrist ligament tears: Evaluation of MRI and combined MDCT and MR arthrography |
101 |
|
11 |
Alefacept treatment in psoriatic arthritis - Reduction of the effector T cell population in peripheral blood and synovial tissue is associated with improvement of clinical signs of arthritis |
101 |
|
12 |
The utility of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex of the wrist |
100 |
|
13 |
Comparison of 3-T MRI and Arthroscopy of Intrinsic Wrist Ligament and TFCC Tears |
98 |
|
14 |
Arthroscopic repair of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears |
95 |
|
15 |
Distal radioulnar instability is an independent worsening factor in distal radial fractures |
90 |
|
16 |
The ulnocarpal stress test in the diagnosis of ulnar-sided wrist pain |
90 |
|
17 |
Isolated tears of the triangular fibrocartilage: Management by early arthroscopic repair |
89 |
|
18 |
Evaluation of chronic wrist paın by arthrography, arthroscopy, and arthrotomy |
89 |
|
19 |
Ulnar shortening for triangular fibrocartilage complex tears associated with ulnar positive variance |
88 |
|
20 |
Arthroscopic resection of dorsal ganglion of the wrist |
82 |
|
21 |
The scapholunate interosseous ligament in MR arthrography of the wrist: Correlation with non-enhanced MRI and wrist arthroscopy |
81 |
|
22 |
Comparison of the findings of triple-injection cinearthrography of the wrist with those of arthroscopy |
81 |
|
23 |
MR imaging diagnosis of triangular fibrocartilage pathology with arthroscopic correlation |
79 |
|
24 |
Limitations of MR Imaging in the diagnosis of peripheral tears of the triangular fibrocartilage of the wrist |
78 |
|
25 |
Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders at the NFL combine-trends from 1987 to 2000 |
77 |
|
26 |
Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist: Diagnostic performance statistics |
77 |
|
27 |
Diagnostic comparison of 1.5 Tesla and 3.0 Tesla preoperative MRI of the wrist in patients with ulnar-sided wrist pain |
76 |
|
28 |
Evaluation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex tears by arthroscopy, arthrography, and magnetic-resonance-imaging |
75 |
|
29 |
Treatment of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius - Fluoroscopic or arthroscopic reduction? |
74 |
|
30 |
Intercarpal ligament injuries associated with fractures of the distal part of the radius |
74 |
|
31 |
The carpal ligaments in MR arthrography of the wrist: Correlation with standard MRI and wrist arthroscopy |
74 |
|
32 |
A comparison of combined arthroscopic triangular fibrocartilage complex debridement and arthroscopic wafer distal ulna resection versus arthroscopic triangular fibrocartilage complex debridement and ulnar shortening osteotomy for ulnocarpal abutment syndrome |
72 |
|
33 |
Internal derangement of the wrist: Indirect MR arthrography versus unenhanced MR imaging |
72 |
|
34 |
New trends in arthroscopic management of type 1-B TFCC injuries with DRUJ instability |
70 |
|
35 |
Ulnar impaction syndrome: MR imaging findings |
70 |
|
36 |
Clinical comparison of arthroscopic versus open repair of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears |
69 |
|
37 |
Results of acute arthroscopically repaired triangular fibrocartilage complex injuries associated with intra-articular distal radius fractures |
68 |
|
38 |
Ulna-shortening osteotomy after failed arthroscopic debridement of the triangular fibrocartilage complex |
68 |
|
39 |
Mr-imaging of anatomy and tears of wrist ligaments |
67 |
|
40 |
Arthroscopic reduction versus fluoroscopic reduction in the management of intra-articular distal radius fractures |
64 |
|
41 |
Direct MR arthrography of the wrist in comparison with arthroscopy: A prospective study on 125 patients |
62 |
|
42 |
Intra-articular distal radius fractures: Arthroscopic assessment of radiographically assisted reduction |
61 |
|
43 |
Lesions of the triangular fibrocartilage complex: MR findings with a three-dimensional gradient-recalled-echo sequence |
61 |
|
44 |
Foveal TFCC Tear Classification and Treatment |
60 |
|
45 |
Partial scapholunate ligament injuries treated with arthroscopic debridement and thermal shrinkage |
59 |
|
46 |
Blatt's capsulodesis for chronic scapholunate dissociation |
59 |
|
47 |
Interosseous ligament tears of the wrist: Comparison of multi-detector row CT arthrography and MR imaging |
58 |
|
48 |
Arthroscopic repair of the triangular fibrocartilage complex |
56 |
|
49 |
Peripheral tear of the triangular fibrocartilage: Depiction with MR arthrography of the distal radioulnar joint |
55 |
|
50 |
New advances in wrist arthroscopy |
54 |
|
51 |
Dry arthroscopy of the wrist: Surgical technique |
54 |
|
52 |
Complications of wrist arthroscopy |
54 |
|
53 |
Extrinsic carpal ligaments: Normal MR arthrographic appearance in cadavers |
54 |
|
54 |
Applied anatomy of the superficial branch of the radial nerve |
53 |
|
55 |
The role of arthroscopy in the treatment of intraarticular wrist fractures |
53 |
|
56 |
Arthroscopic versus open dorsal ganglion excision: A prospective, Randomized comparison of rates of recurrence and of residual pain |
52 |
|
57 |
Current concepts in wrist arthroscopy |
52 |
|
58 |
Comparison between high-resolution MRI with a microscopy coil and arthroscopy in triangular fibrocartilage complex injury |
52 |
|
59 |
Wrist arthroscopy for the treatment of ligament and triangular fibrocartilage complex injuries |
52 |
|
60 |
Arthroscopically assisted reduction of intraarticular distal radial fractures |
52 |
|
61 |
The radial sensory nerve - an anatomic study |
52 |
|
62 |
Mr evaluation of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears in the wrist - comparison with arthrography and arthroscopy |
52 |
|
63 |
Prospective Outcomes and Associations of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Resected Arthroscopically |
51 |
|
64 |
3.0 T high-resolution MR imaging of carpal ligaments and TFCC |
51 |
|
65 |
Results of repair of peripheral tears in the triangular fibrocartilage complex using an arthroscopic suture technique |
51 |
|
66 |
Wrist arthrography versus arthroscopy: A comparative study of 150 cases |
51 |
|
67 |
Comparison of Arthroscopic and Open Treatment of Septic Arthritis of the Wrist |
49 |
|
68 |
A comparison of the findings of wrist arthroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging in the investigation of wrist pain |
49 |
|
69 |
A comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopy in the investigation of chronic wrist pain |
49 |
|
70 |
Arthroscopic management of wrist triangular fibrocartilage complex injuries in the athlete |
49 |
|
71 |
Intrinsic ligament and triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears of the wrist: comparison of isovolumetric 3D-THRIVE sequence MR arthrography and conventional MR image at 3 T |
48 |
|
72 |
Arthroscopy-assisted fracture fixation |
48 |
|
73 |
Wrist arthroscopy - indıcations and results |
48 |
|
74 |
Intrinsic ligament and triangular fibrocartilage complex tears of the wrist: comparison of MDCT arthrography, conventional 3-T MRI, and MR arthrography |
47 |
|
75 |
Arthroscopic resection in the management of dorsal wrist ganglions: Results with a minimum 2-year follow-up period |
47 |
|
76 |
Arthroscopic portals of the wrist - an anatomic study |
46 |
|
77 |
The application of indirect reduction techniques in the distal radius: The role of adjuvant arthroscopy |
45 |
|
78 |
Press test for office diagnosis of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears of the wrist |
45 |
|
79 |
A comparison of CT arthrography of the wrist to findings during wrist arthroscopy |
44 |
|
80 |
Chronic lunotriquetral instability – diagnosıs and treatment |
44 |
|
81 |
MRI in the diagnosis of cartilage injury in the wrist |
43 |
|
82 |
Percutaneous fixation of scaphoid fractures |
43 |
|
83 |
Treatment of isolated injuries of the lunotriquetral ligament - A comparison of arthrodesis, ligament reconstruction and ligament repair |
43 |
|
84 |
The effect of observer experience on magnetic resonance imaging interpretation and localization of triangular fibrocartilage complex lesions |
43 |
|
85 |
Wrist ligament injuries: value of post-arthrography computed tomography |
42 |
|
86 |
Diagnostic accuracy of plain radiographs and cineradiography in diagnosing traumatic scapholunate dissociation |
40 |
|
87 |
Association between extrinsic and intrinsic carpal ligament injuries at MR arthrography and carpal instability at radiography: Initial observations |
40 |
|
88 |
Early isolated triangular fibrocartilage complex tears: Management by arthroscopic repair |
40 |
|
89 |
Diagnostic usefulness of synovial vascular morphology in chronic arthritis. A systematic survey of 100 cases |
39 |
|
90 |
Arthroscopically Assisted Repair of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Foveal Tears |
38 |
|
91 |
The Natural Course of Traumatic Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears in Distal Radial Fractures: A 13–15 Year Follow-up of Arthroscopically Diagnosed but Untreated Injuries |
38 |
|
92 |
Arthroscopic Treatment of Peripheral Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears With the Deep Fibers Intact |
38 |
|
93 |
Arthroscopic Treatment of Triangular Fibrocartilage Wrist Injuries in the Athlete |
38 |
|
94 |
Standard wrist arthroscopy. Technique and documentation |
37 |
|
95 |
Arthroscopically Assisted Reattachment of Avulsed Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex to the Fovea of the Ulnar Head |
37 |
|
96 |
Triangular fibrocartilage injuries in pediatric and adolescent patients |
37 |
|
97 |
Instability of the Distal Radioulnar Joint - an Overview of Clinical and Radiological Procedures Regarding their Efficacies |
36 |
|
98 |
Arthroscopic Resection of Dorsal Wrist Ganglia: 114 Cases With Minimum Follow-Up of 2 Years |
36 |
|
99 |
High-resolution MR imaging of triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC): comparison of microscopy coils and a conventional small surface coil |
36 |
|
100 |
MRI versus arthroscopy in the diagnosis of scapholunate ligament injury |
35 |
Table 2.
All articles were published in 28 different journals, with the Journal of Hand Surgery-American volume contributing the most 28 (28%), followed by Arthroscopy: Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 13 (13%), Radiology 7 (7), American Journal of Roentgenolgy 6 (6), Journal of Hand Surgery-British and Europan volume 5 (5%), Skeletal Radiology 5 (5%), The journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (American Volume) 4 (4%), Hand Clinics 4 (4%), Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research 3 (3%), Arthritis and Rheumatism 3 (3%), The journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (British Volume) 2 (2%), RoFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Rontgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren 2 (2%), Handchirurgie Mikrochirurgie Plastische Cirurgie 1 (1%), Operative Orthopädie und Traumatologie 1 (1%), Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 1 (1%), American Journal of Sports Medicine 1 (1%), Clinical Radiology 1 (1%), Annals of Plastic Surgery 1 (1%), The Journal of Trauma Injury Infection and Critical Care 1 (1%), Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy 1 (1%), Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1 (1%), Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1 (1%), Orthopedics 1 (1%), Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery 1 (1%), Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography 1 (1%), Clinical Anatomy 1 (1%), Radiographics 1 (1%), Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 1 (1%), British Medical Bulletin 1 (1%), BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 1 (1%), respectively.
According to the origins of the journals where the articles were published, there were 44 articles about orthopedics, 26 articles about radiology and nuclear medicine, 14 articles about sports science, 7 articles about surgery, and 4 articles about rheumatology. The remaining 5 articles were about emergency medicine, general internal medicine, anatomy and morphology, critical care medicine, and rehabilitation, respectively.
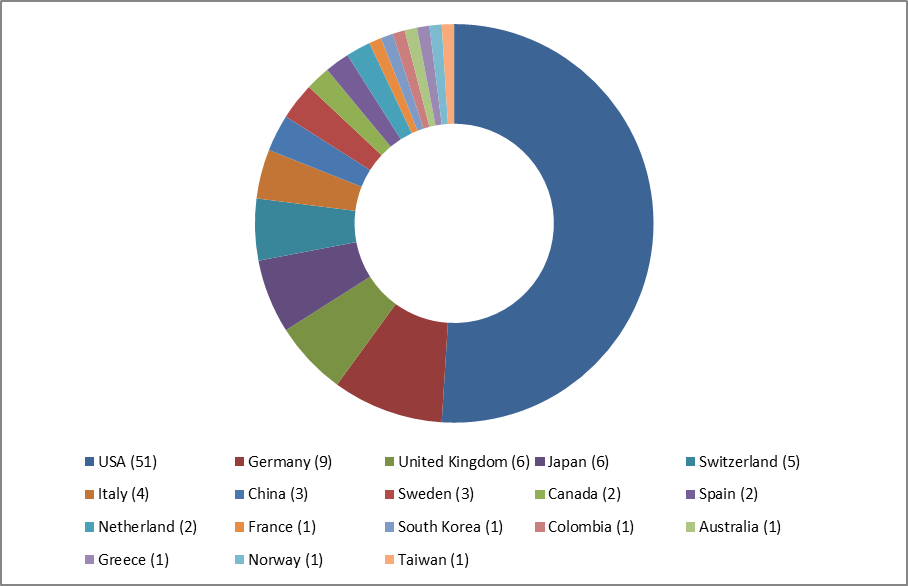
The most prolific years were 2001 with 9 articles published, followed by the years 2007 and 2008 with 8 articles published in each. There were articles from 18 different countries and 71 different institutes. The most productive institutes were Mayo Clinic from the United States of America (USA) with 8 publications; Wake Forest University, Yale University, and Brown University from the USA with 4 publications each (Table 3). In terms of country and region of origin, most articles were from the United States of America (51), which was followed by Germany (9), the United Kingdom (6), Japan (6), Switzerland (5), and Italy (4) (Table 4).
|
Institution |
Record Count |
|---|---|
|
Mayo clinic |
8 |
|
Wake Forest University |
4 |
|
Brown University |
4 |
|
Yale University |
4 |
|
ChineseUniversity of Hong Kong |
3 |
|
Nagoya University |
3 |
|
Lund University |
3 |
|
Heinrich-HeineUniversity of Dusseldorf |
2 |
|
University of Amsterdam |
2 |
|
Hospital for Special Surgery, New york |
2 |
|
HokkaidoUniversity |
2 |
|
University of Pennsylvania |
2 |
|
University of Modena |
2 |
|
Balgrist University Hospital |
2 |
|
Others |
57 |
Table 4.
The most cited article was the article by Cooney WP et al. published in the Journal of Hand Surgery-American Edition with 180 citations [13]. The most-cited author was Cooney, WP, who had published 2 articles (2%). The total number of citations associated with Cooney WP was 269. The topic of the most cited article included the diagnosis and treatment of TFCC (13).
Among the 100 most cited articles, 86 were identified as original articles, 6 were review articles, 7 were cadaveric studies and 1 was a clinical trial. Based on the criteria on level of evidence, 5 articles were providing Level I evidence, 14 articles providing level II evidence, 36 articles providing level III evidence, 36 articles providing level IV evidence, and 9 articles providing level V evidence.
Among the 100 most cited articles, the 5 most discussed main topics were as follows: 1) The use of Magnetic resonanas imaging (MRI), arthroscopy, and arthrography in the diagnosis of the wrist − 33 (33%), 2) The diagnosis and treatment of TFCC injuries − 24 (24%), 3) Arthroscopic intercarpal ligament repair − 11 (11%), 4) Arthroscopy-assisted fracture fixation − 10 ( 10%), and 5) Arthroscopic excision of the ganglion cysts on the wrist − 6 (6%).