To our knowledge, this study was among one of the first studies with respect to the psychological responses of the delivery women in mainland China. The prevalence rate of PPD was as high as 30.0%. The present figure was higher than the prevalence of PPD reported in other studies carried out in China using the EPDS scale[17-19]. For example, in Hebei province of north China, 20.3% of women had elevated levels of postpartum depressive symptoms[17]. In Shanghai of east China, the estimated prevalence of PPD 6 weeks after delivery was 11.8%[18]. In Guangzhou of south China, the rate of PPD was 27.4%[19]. However, our result is consistent with reports in Asian countries which indicated the prevalence of PPD ranged from 3.5% to 63.3%[20]. Another cross-sectional study in Brazil also found a similar prevalence of PPD (27.9%) among low income women[10]. Higher rates of PPD in this study may be explained by two evident differences between other studies and the current one. First, the present data were obtained during the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the COVID-19 outbreak in Guangzhou may not be regarded as severe, the number of imported cases is increasing during the time the study was conducted. According to Behavioral Immune System theory, people are likely to develop negative emotions and avoidant behaviors when faced with public health emergencies[11]. The uncertainty and unpredictability of COVID-19 may cause cognitive dissonance and insecurity, thus providing a feeling of mental discomfort. In addition, with the closure of schools and business as well as social-distancing regulations, negative emotions experienced by individuals are compounded. Therefore, these COVID-19 related factors have helped to add the stressful impact on women’s mental health. Second, the present study was entirely drawn from Guangzhou, one of the most affluent metropolis in south China. As Guangzhou is one of the major air transportation hubs with more than 130 international flights connecting main countries in the world, the potential impact of global COVID-19 outbreak is high. Moreover, with the lockdown eased gradually to ensure smooth resumption of work and production, internal migrants who were originally from the large poor and rural areas in the western and central inland provinces migrated to the southern developed regions, such as Guangzhou for better job opportunities and income. The convenience of long-distance travel could increase the incidence of local cases through respiratory droplets (e.g., from exhalation sneeze) and contact routes[21]. And the possibility of transmission by asymptomatic carriers could further enhance it's spread[21]. Such occurrences of both imported cases and domestically transmitted cases have significant potential for psychological contagion, resulting in widespread fear, helplessness, and a variety of adverse mental health outcomes[7].
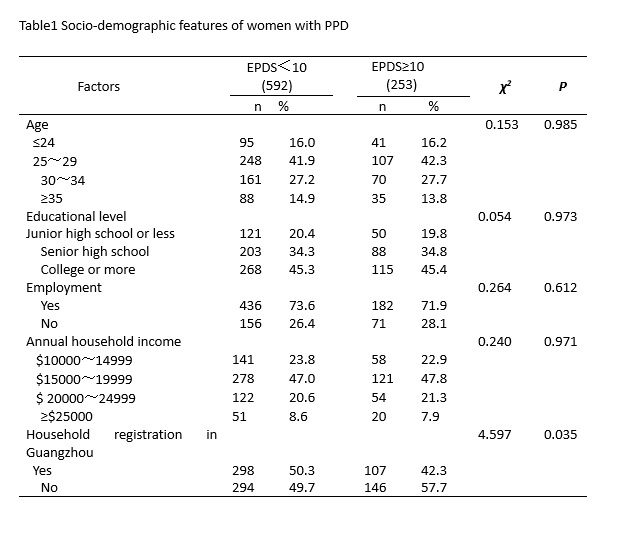
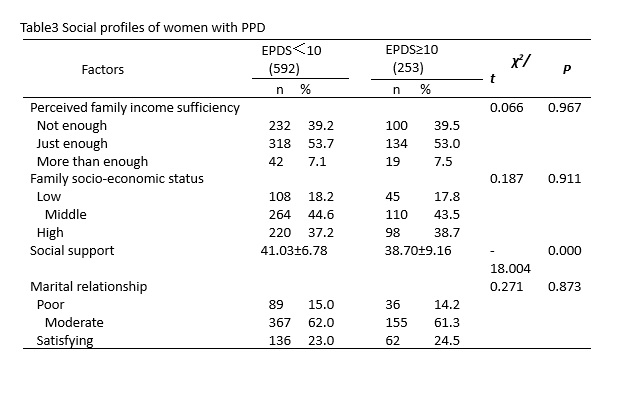
The findings of this study showed that immigrant women were significantly more likely to develop PPD compared to local registered women, which was consistent with the findings of previous studies that immigrant women were at increased risk of depression perinatally[22]. Due to long-standing household registration policy in China, internal migrants do not have the same rights and benefits as local residents in a variety of areas, such as healthcare, social services, education and employment. We hypothesized social exclusion resulting from this policy as well as other economic and cultural factors have an impact on mental health of immigrants. We also reported a strong association between social support and PPD which was consistent with a previous study [19]. One possible reason is that during the pandemic, the pace of the whole society is slowed down. This could have been created more opportunities and time for family member to support and care for each other. In addition, communication with community members and friends was increased because people were asked to stay at home instead of going to public places. These positive impacts may have helped women cope with the challenges surrounding the postpartum period.
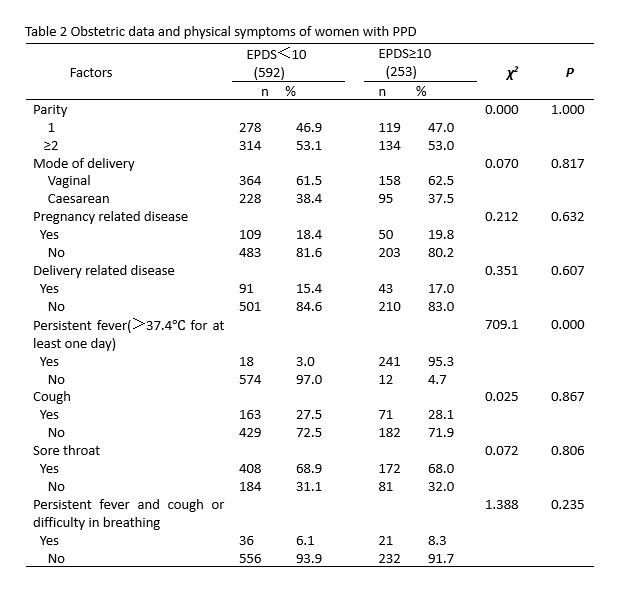
In addition, we explored the relationship between mental health and physical symptoms as well as concerns about COVID-19 among delivery women during the pandemic. The presence of a persistent fever was significantly associated with PPD. Similarly, a higher perceived likelihood of contracting COVID-19 during the current outbreak was significantly associated with PPD. Amid this moment, women were bombarded with various discomforting network information about COVID-19, including clinical signs, routes of transmission, medicines or vaccines, et al. After presentation to the clinic with a fever, they may be sent home, hospitalized for further observation, or quarantined. Some evidences suggest that up-to-date and accurate information during the pandemic is responsible for lower levels of stress, anxiety and depression[7]. Moreover, higher satisfaction with the health information received by the whole population is contributing to the reduced impact of rumors and this may avoid adverse psychological reactions.
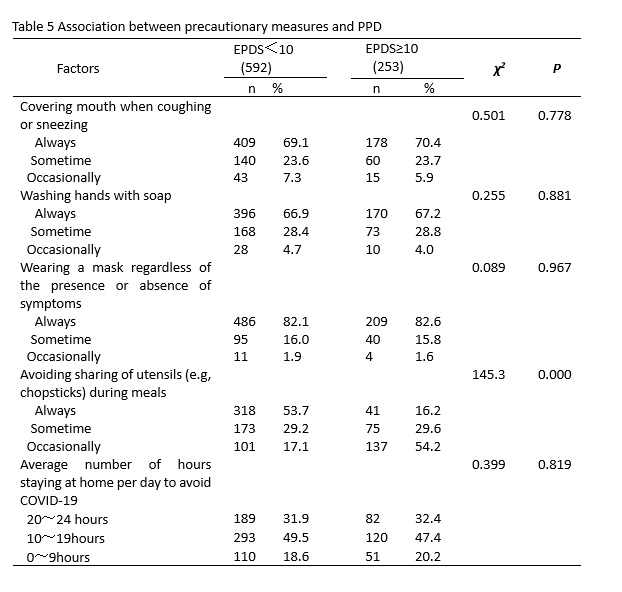
Also, our findings suggest that precautionary measures adopted to prevent the spread of COVID-19 have had a positive psychological effect. Women who had avoided the sharing of utensils (e.g, chopsticks) during meals were significantly less likely to develop PPD. There has been no evidence to suggest the reason for the difference, but saliva is one of the most common ways for food-borne diseases to spread. Communal eating habits have been a part of Chinese culture for centuries. Chinese people prefer to using chopsticks to pick up food commonly shared in the table during meal times to show their respect. The experiences of the SARS-COV epidemic in 2013 may have changed the perception of the general public towards precautionary measures. Many cities in China have already launched initiatives to order separate meals. As this healthy habit is related to people's health and safety during the pandemic, it's not unexpected that avoidance of sharing utensils during meals is significantly associated with less psychological impact on women.
Our findings will provide vital guidance for health care professionals to tackle mental health issues among delivery women during a pandemic. First, health authorities need to identify high-risk groups such as immigrants for early intervention. Second, accurate and up-to-date health information during the pandemic needs to be provided in order to alleviate the concern and reduce the impact of rumors. Third, government and health authorities need to expand public awareness of healthy lifestyle.
This study has several limitations. First, a cross-sectional study did not allow for establishing causal relationships between PPD and the factors associated with it. Second, a self-reported scale was employed to define PPD instead of clinician administered structured interview. Participants might have provided responses they feel socially desirable. Third, the short time frame might not allow us to observe it's long-term impacts on mental health among delivery women.